Advanced LCA Research Group
Advanced LCA Research Group

5 Researchers:
Keiichiro Sakurai, Kyoko Ono, Yoon-Young Chun, Naoya Kojima
4 Contract Employees
Outline
We are conducting risk assessments and life cycle assessments (LCAs) to evaluate the potential issues posed by new technologies, with the aim of providing evidence to support better decision-making for building a sustainable society. Specifically, we are conducting a risk trade-off analysis considering the product life cycle of chemicals, as well as risk assessments s related to disasters and accidents. Additionally, we are developing evaluation methods to analyze socio-economic impacts, spillover effects, and social acceptability. Our research covers a wide range of topics, including carbon neutral and energy-related technologies, nitrogen cycle technologies, and the introduction of marine biodegradable plastics.
Furthermore, we are advancing research on statistical methods, which form the foundation of many industries.
Research Highlights
Risk management of plastic for the Circular Economy
To accelerate the transition to a plastic circular economy, there is growing interest in the health impact by additives and contaminants specific to recycled plastic. For the final goal of proposing a management strategy, we aim to understand the entire life cycle of plastic and to conduct exposure assessments and risk evaluation of its additives and contaminants.
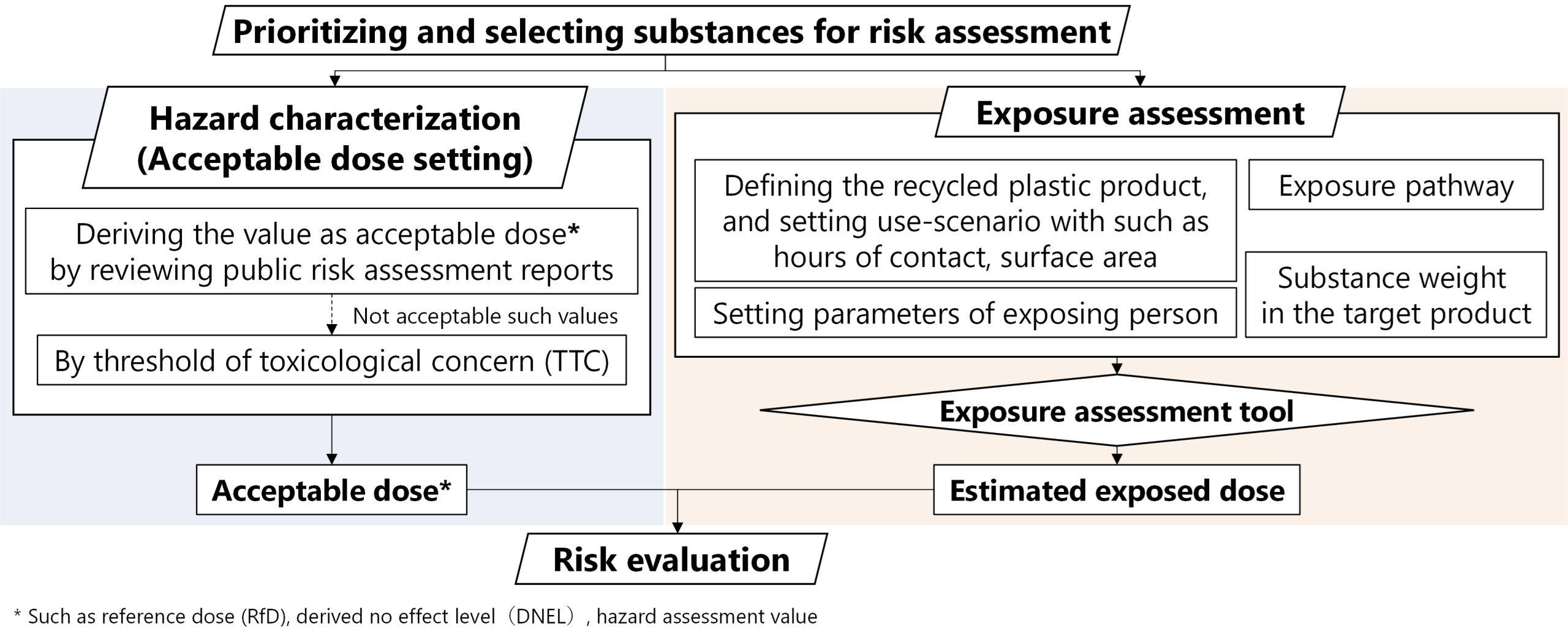
Risk assessment framework for recycled plastics
Risk evaluation and risk management for ammonia fuel
We conduct risk assessments for the leakage of ammonia fuel, which is expected to be stored and used in larger quantities. Notably, we estimated the leak frequency for ammonia-fueled vessels based on the Bayesian theorem derived from onshore ammonia dealing facilities extracted from the Japanese accident database.
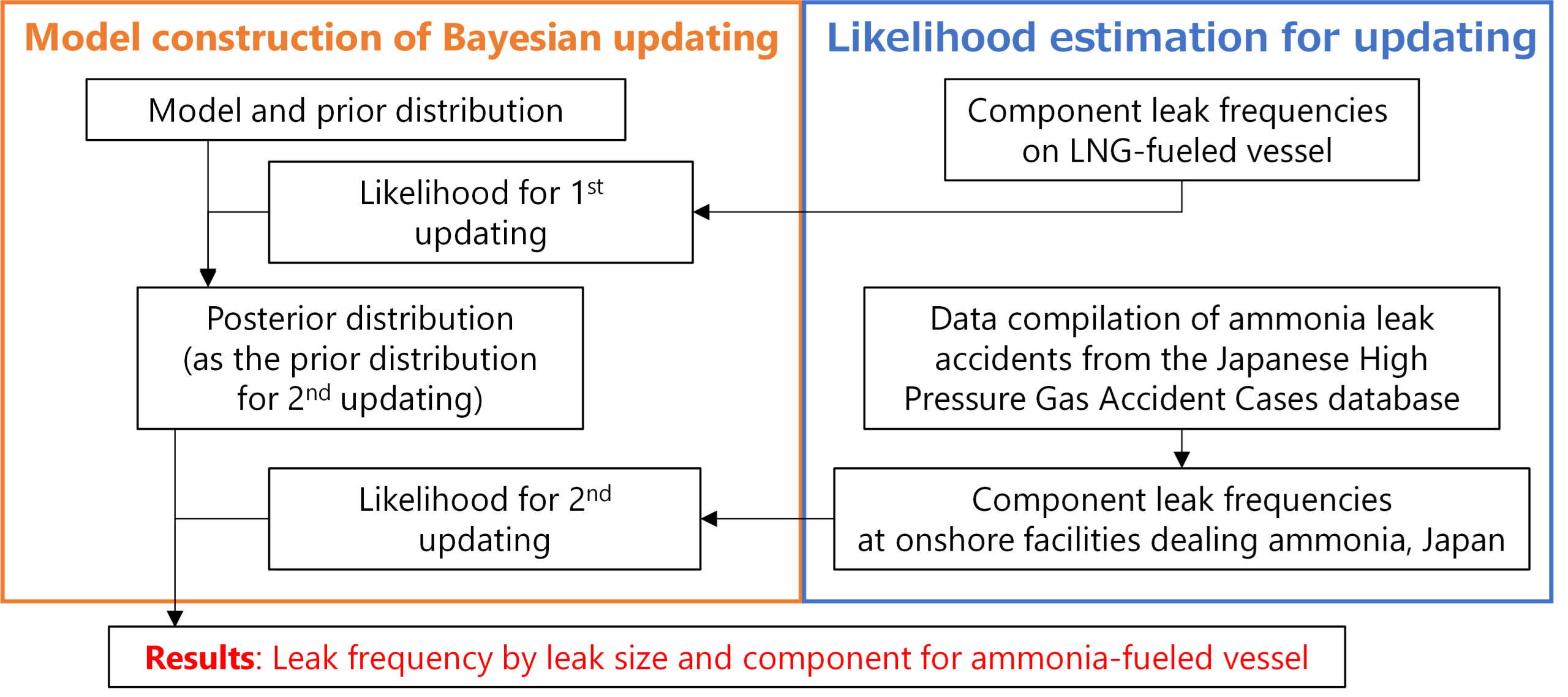
Overview of leak frequency estimation for ammonia fuel ships
Finding pathways for the accelerated deployment of energy technologies
To achieve a sustainable society, technologies such as energy-efficient buildings, renewables, and electrical vehicles are not enough on their own. Strategies for smooth deployment are also required. We research these strategies to maximize the societal benefits of new technologies.

Figure: A proposed scenario for global deployment of photovoltaics (PV) to achieve 75TW of cumulative capacity by 2050. Historical and projected installation suggest this scenario is achievable. |
Understanding Public Acceptance of Energy Harvesting Technology from Radioactive Waste
Energy harvesting technology from radioactive waste can be an innovative and sustainable energy solution. However, the public’s negative perception and low acceptance of radioactivity and related technologies are barriers to realizing this idea. This study aims to understand and analyze public acceptance, attitudes, and perceptions of energy harvesting technology from radioactive waste.

Energy harvesting technology acceptance model for Japanese residents |
We develop a model to test if and how underlying factors (perceived risk, perceived benefit, perceived knowledge, social trust, and environmental concern) affect public acceptance of energy harvesting technology from already existing radioactive waste.
International Standardization Activities on the Application of Statistical Methods
The application of statistical methods, which forms the foundation of many industries, including statistical quality control, is being standardized by the International Organization for Standardization Technical Committee 69 (ISO/TC69). We are deeply involved in this activity, contributing to the creation of international rules regarding statistical terminology and symbols, methods for the statistical interpretation of data, and statistical methods for quantifying the accuracy of measurement (testing) methods. Additionally, we are engaged in researching related methods that have been required during discussions in this activity.

ISO TC69 Plenary Meeting

